Changing Trends and Careers in Physical Education
1. Concept, Aims & Objectives of Physical Education
2. Developmen t of Physical Education in India – Post Independenc e
3. Changing Trends in Sports- playing surface, wearable gear and sports equipment, technological advancements
4. Career options in Physical Education
5. Khelo-India Program and Fit – India Program
1. Concept of Physical Education
Physical Education is education through physical activities for the comprehensive development of an individual's total personality – physically, mentally, emotionally, and socially. It's an academic subject taught in schools and other educational institutions worldwide, aiming to provide students with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes necessary for a physically active and healthy life.
Defined Physical Education:
Charles A. Bucher defined it as "an integral part of the total educational process... a field of endeavour that has as its aim the improvement of human performance through the medium of physical activities that have been selected with a view to realizing this outcome"
Aim of Physical Education:
Physical Education, at its core, refers to education achieved through physical activities with the ultimate goal of fostering the all-round development of an individual.
According to the National Plan of Physical Education and Recreation, the aim is "to make every child physically, mentally and emotionally fit and also to develop in him such personal and social qualities as will help him to live happily with others and build him up as a good citizen"
Objectives of Physical Education
The objectives of a well-designed Physical Education program are multifaceted, aiming for holistic development:
a. Physical Objectives
- Develop physical fitness components (strength, endurance, flexibility, agility, and speed).
- Improve motor skills (running, jumping, throwing, catching, etc.).
- Enhance body coordination and balance.
- Promote cardiovascular health and muscular efficiency.
b. Cognitive Objectives
- Teach rules, strategies, and tactics of various sports and activities.
- Enhance understanding of health, fitness, and nutrition principles.
- Develop critical thinking and decision-making skills during physical activities.
- Foster awareness of safety practices in sports and exercises.
c. Affective (Emotional) Objectives
- Build self-esteem and confidence through achievement in physical activities.
- Encourage positive attitudes toward fitness and health.
- Develop emotional control and resilience in competitive and challenging situations.
- Promote enjoyment and satisfaction in physical activities.
d. Social Objectives
- Encourage teamwork, cooperation, and communication skills.
- Develop leadership qualities and the ability to follow rules.
- Foster respect for peers, opponents, and officials.
- Promote social integration and inclusivity through group activities.
Summary
The concept of Physical Education revolves around holistic development through physical activity. Its aims focus on fostering physical fitness, mental sharpness, emotional balance, and social skills for a healthy lifestyle. The objectives are specific goals across physical, cognitive, affective, and social domains, ensuring individuals become well-rounded, active, and responsible members of society.
2. Development t of Physical Education in India – Post Independence
Below are the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) on the Development of Physical Education in India – Post Independence with correct answers and brief explanations:
- When was the Central Government Physical Education Committee, also known as the Tara Chand Committee, established?
a) 1947
b) 1948
c) 1950
d) 1951
Answer: b) 1948
Explanation: The Tara Chand Committee was formed in 1948 to recommend measures for improving physical education in India, including establishing training colleges. - The Central Advisory Board of Physical Education, formed in 1950, aimed to introduce Physical Education as a compulsory subject at which levels?
a) Only elementary level
b) Only senior secondary level
c) Elementary, middle, and senior secondary levels
d) Only college level
Answer: c) Elementary, middle, and senior secondary levels
Explanation: The Board advised making physical education compulsory across elementary, middle, and senior secondary levels to promote holistic development. - In which city were the First Asian Games held in 1951?
a) Mumbai
b) Kolkata
c) New Delhi
d) Chennai
Answer: c) New Delhi
Explanation: The First Asian Games were hosted in New Delhi in 1951, marking a significant milestone in India’s post-independence sports history. - Who introduced the Coaching Scheme for games and sports in India in 1953?
a) Tara Chand
b) Rajkumari Amrit Kaur
c) Jawaharlal Nehru
d) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
Answer: b) Rajkumari Amrit Kaur
Explanation: Rajkumari Amrit Kaur, the then Health Minister, initiated the Rajkumari Coaching Scheme in 1953 to develop sports training. - The National Institute of Sports (NIS) was established in 1961 in Patiala, Punjab, primarily to:
a) Organize international competitions
b) Develop sports infrastructure
c) Produce qualified coaches
d) Promote indigenous games
Answer: c) Produce qualified coaches
Explanation: NIS (now Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports) was set up to train coaches and enhance sports expertise. - Which institution was originally established as Lakshmibai College of Physical Education (LCPE) in 1957?
a) National Institute of Sports
b) Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE)
c) Sports Authority of India
d) All India Council of Sports
Answer: b) Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE)
Explanation: LCPE, established in 1957 in Gwalior, later became LNIPE. - When did Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education (LNCPE) gain "Deemed University" status under the name LNIPE?
a) 1973
b) 1984
c) 1995
d) 2010
Answer: c) 1995
Explanation: LNCPE was granted Deemed University status in 1995, becoming LNIPE. - The National Physical Efficiency Drive was sponsored by the Ministry of Education in 1959 to:
a) Promote competitive sports
b) Evaluate the physical fitness status of people
c) Develop new sports facilities
d) Introduce yoga in schools
Answer: b) Evaluate the physical fitness status of people
Explanation: The Drive aimed to assess and improve the physical fitness of the population. - When was the National Fitness Corps established with the objective of making youth physically strong?
a) 1959
b) 1965
c) 1970
d) 1975
Answer: b) 1965
Explanation: The National Fitness Corps was formed in 1965 to enhance youth fitness. - The Sports Talent Search Scheme and Rural Sports Tournament Scheme were introduced in:
a) 1965
b) 1970-71
c) 1975
d) 1982
Answer: b) 1970-71
Explanation: These schemes were launched in 1970-71 to identify and nurture sports talent, especially in rural areas. - When was the Sports Authority of India (SAI) established?
a) 1975
b) 1982
c) 1984
d) 1987
Answer: c) 1984
Explanation: SAI was established in 1984 to promote sports and support athletes. - The Society for National Institutes of Physical Education and Sports (SNIPES) was merged with SAI in which year?
a) 1984
b) 1987
c) 1995
d) 2010
Answer: b) 1987
Explanation: SNIPES was merged with SAI in 1987 to streamline sports administration. - In which year did CBSE make Physical Education a compulsory subject for classes IX to XII?
a) 2010
b) 2017
c) 2018
d) 2019
Answer: c) 2018
Explanation: CBSE mandated Physical Education as compulsory for classes IX to XII in 2018. - From April 2019, CBSE mandated a daily Health and Physical Education period for which classes?
a) Classes IX to XII
b) Classes VI to VIII
c) Classes 1st to 8th
d) All classes (1st to 12th)
Answer: d) All classes (1st to 12th)
Explanation: CBSE introduced a daily Health and Physical Education period for all classes from April 2019. - The Khelo India Programme was launched by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports in the financial year:
a) 2016-2017
b) 2017-2018
c) 2018-2019
d) 2019-2020
Answer: b) 2017-2018
Explanation: The Khelo India Programme was launched in 2017-2018 to promote grassroots sports. - What is the budget allocation for the Khelo India Programme for the period of 2017-18 to 2019-20?
a) Rs. 1,000 Crore
b) Rs. 1,756 Crore
c) Rs. 2,000 Crore
d) Rs. 2,500 Crore
Answer: b) Rs. 1,756 Crore
Explanation: The budget for Khelo India from 2017-18 to 2019-20 was Rs. 1,756 Crore. - How many verticals (components) does the Khelo India Programme outline?
a) Ten
b) Eleven
c) Twelve
d) Thirteen
Answer: c) Twelve
Explanation: The Khelo India Programme has twelve components, including talent identification and sports infrastructure development. - The Fit India Movement was introduced by the Hon’ble Prime Minister on:
a) January 26, 2019
b) August 15, 2019
c) August 29, 2019
d) October 2, 2019
Answer: c) August 29, 2019
Explanation: The Fit India Movement was launched on August 29, 2019, to promote fitness nationwide. - Which of the following is NOT an objective of the Fit India Movement?
a) To promote fitness as easy, fun, and free
b) To spread awareness on fitness through focused campaigns
c) To encourage indigenous sports
d) To identify and train elite athletes for international competitions
Answer: d) To identify and train elite athletes for international competitions
Explanation: The Fit India Movement focuses on general fitness and awareness, not elite athlete training. - According to the Khelo India Programme, what is the annual financial assistance provided to selected talented players for 8 years?
a) Rs. 1 Lakh
b) Rs. 2.5 Lakhs
c) Rs. 5 Lakhs
d) Rs. 10 Lakhs
Answer: c) Rs. 5 Lakhs
Explanation: Selected players under Khelo India receive Rs. 5 Lakhs annually for 8 years to support their training.
Changing Trends in Playing Surfaces
Playing surfaces for sports and physical activities have evolved due to sport requirements, location, climate, and infrastructure needs.
- Outdoor Sports:
- Athletic Jogging Tracks: Shifted from clay/cinder to synthetic rubber surfaces (latex/polyurethane on asphalt/concrete) for better traction and low maintenance.
- Turf: Natural grass/clay replaced by synthetic options like Polygrass (for football) and Astroturf (for hockey) for durability and faster play.
- Multi Utility Games Area (MUGA): Synthetic rubber surfaces with shock absorbency, ideal for playgrounds, recreational areas, and outdoor gyms in urban settings.
- Indoor Sports:
- Indoor Courts: Synthetic or wooden surfaces for badminton, basketball, and handball, enabling year-round play.
- Indoor MUGA: Durable rubberized surfaces for multiple activities, ensuring safety and versatility.
Changing Trends in Wearable Gears and Sports Equipment
Advancements in wearable gears and equipment enhance safety, performance, monitoring, and aesthetics.
- Safety: Lighter, stronger helmets, gloves, and guards made from advanced materials for better protection.
- Performance: Friction-reducing swimsuits, aerodynamic footwear, and boots improve efficiency.
- Monitoring & Judgement: GPS and wearable devices track body chemistry and performance for real-time coaching.
- Aesthetics: Trendy athletic apparel boosts confidence and image, driven by media and marketing.
Technological Advancements in Sports
Technology has transformed officiating, safety, performance analysis, and event management in sports.
- Officiating Technology:
- LED lights (e.g., cricket stumps) aid decision-making.
- Infra-red (Hot Spot) detects ball contact in cricket.
- Video replays, slow motion, and VAR assist referees in multiple sports.
- Laser technology ensures precise foul detection (e.g., gymnastics scoring, long jump).
- Protective Equipment: Advanced materials create safer, comfortable gear (e.g., cricket helmets).
- Timing Systems: GATES, lasers, and touch sensors provide precise race timings.
- Location Tracking: GPS tracks player movements and aids crowd management in stadiums.
- Biomechanical Analysis: Software, sensors on equipment, and force plates analyze movement, swing speed, power, and ground reaction forces for technique improvement.
Academic Courses in Physical Education
The National Council of
Teacher Education (NCTE) recognizes several essential courses for aspiring
Physical Education teachers:
- Diploma in Physical Education (D.P.Ed.): Aimed at preparing educators for
elementary-level teaching (Classes I-VIII).
- Bachelor of Physical Education (B.P.Ed.): This program qualifies individuals to teach
theoretical concepts in Classes VI-X and manage sports activities for
Classes XI-XII.
- Master of Physical Education (M.P.Ed.): Designed for training teachers for senior
secondary education (Classes XI-XII), as well as roles such as Assistant
Professors, Directors, Sports Officers, or Teacher Educators in colleges
and universities.
Research-Oriented Programs:
- Master of Philosophy (M.Phil.)
- Doctorate of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
- Post Doctorate Fellowship (P.D.F.)
Other
UGC/Institute-Recognized Courses:
- Post Graduate Diploma Courses: Covering areas like Adventure Sports
Administration, Disability Sports, Fitness Management, Sports Coaching,
Sports Journalism, Sports Management, Sports Nutrition, and Yoga
Education.
- Bachelor’s Courses: Including B.A. in Sports & Performance,
B.P.E., and B.Sc. in Exercise Physiology, Physical Education, or Health
Education and Sports Sciences.
- Master’s Courses: Such as M.B.A. in Sports Management, M.Tech. in
Sports Technology, and M.A./M.Sc. in various specialized fields of
Physical Education.
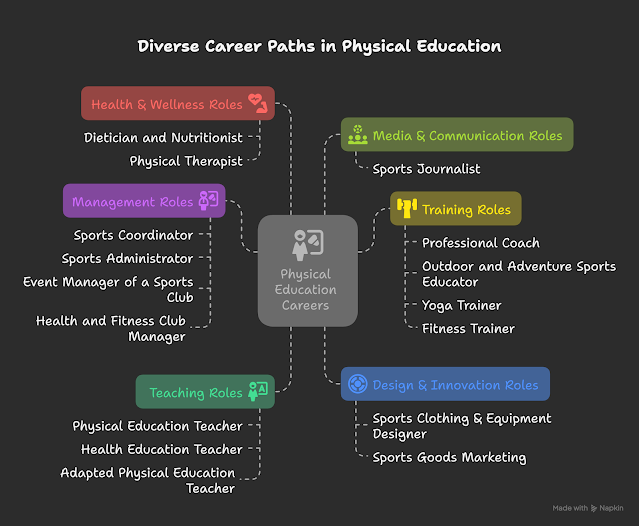
4.Specific Career Options in Physical Education
Graduates can explore
numerous roles that leverage recent advancements in technology, playing
surfaces, and wearable devices:
- Physical Education Teacher (PET): Responsible for teaching at various school
levels, utilizing facilities like synthetic tracks and multi-use games
areas (MUGA).
- Health Education Teacher: Focuses on educating students about health and
fitness, integrating knowledge of sports nutrition and wearable tech for
monitoring health metrics.
- Sports Coordinator: Manages sports programs on advanced surfaces,
utilizing performance tracking technologies for effective team management.
- Professional Coach: Employs biomechanical analysis and sensor
technologies to enhance athlete training and performance.
- Outdoor and Adventure Sports Educator: Teaches adventure sports, ensuring safety
through the use of specialized gear on MUGA surfaces.
- Sports Administrator: Oversees sports facilities, employing modern
technologies for efficient management and officiating.
- Recreational Services Provider: Manages clubs and parks that feature advanced
playing surfaces and safety equipment.
- Event Manager of a Sports Club: Plans and executes sports events using
technology for crowd management and officiating.
- Health and Fitness Club Manager: Operates gyms equipped with modern surfaces,
applying wearable technology for client fitness tracking.
- Sports Clothing & Equipment Designer: Innovates apparel and gear tailored for modern
sports environments, emphasizing performance enhancement.
- Dietician and Nutritionist: Develops nutrition plans for athletes,
utilizing data from wearable devices for personalized diets.
- Sports Goods Marketing: Engages in marketing advanced sports equipment
designed for contemporary playing surfaces.
- Yoga Trainer: Conducts yoga sessions in specialized facilities, using technology
for movement analysis and correction.
- Fitness Trainer: Implements biomechanical tools to optimize training regimens on
modern surfaces.
- Physical Therapist: Utilizes advanced analysis for rehabilitation
of athletes, focusing on injury prevention and recovery.
- Sports Journalist: Covers sporting events, integrating insights
gained from advanced officiating technologies and analytics.
- Adapted Physical Education Teacher: Designs inclusive programs for individuals with
disabilities, using accessible surfaces and specialized equipment.
5. Khelo-India Program and Fit – India Program
Khelo India Program
The Khelo India Program
was initiated to foster a sports culture in India, particularly at the
grassroots level, aiming to position India as a formidable sporting nation.
Launched by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports in the financial
year 2017-2018, the program received cabinet approval on September 20, 2017,
with a significant budget allocation of Rs. 1,756 Crore for the period
from 2017-18 to 2019-20.
Vision and Mission
- Vision:
To enhance the sports culture in India, especially at grassroots levels,
and achieve sporting excellence.
- Mission:
To promote sports across all demographics, emphasizing holistic
development, community integration, gender equality, healthy lifestyles,
national pride, and economic opportunities related to sports.
Aim and Objectives
The primary goal of the Khelo
India Program is to develop a sporting culture, identify and nurture talent
from grassroots to elite levels. The program outlines twelve key verticals:
- Play Field Development: Financial support for the development and
maintenance of sports infrastructure, with funding up to Rs. 50 Lakhs for
States/UTs.
- Community Coaching Development: Training approximately 2000 Physical Education
Teachers (PETs) annually to serve as master trainers for community
coaching.
- State Level Khelo India Centres: Establishing centers using existing resources
for day boarding schemes and online coaching.
- Annual Sports Competitions: Organizing events like the Khelo India National
School Games and National University Games to spot and develop talent.
- Talent Identification and Development: Focusing on 16 priority sports to select
players who receive financial support for training.
- Utilization and Upgradation of Sports
Infrastructure: Grants for
developing critical sports facilities where needed.
- Support to National/Regional/State Sports
Academies: Financial aid to
public and private sports academies.
- Physical Fitness of School Children: Implementing national fitness parameters and
assessment kits in schools.
- Sports for Women: Promoting gender equality in sports and
organizing national competitions specifically for women.
- Sports for Peace and Development: Enhancing sports facilities in
conflict-affected areas and engaging youth through competitions.
- Promotion of Sports for Persons with Disabilities: Financial assistance for specialized
infrastructure and competitions.
- Promotion of Rural and Indigenous/Tribal Games: Organizing competitions to encourage
participation in traditional sports.
Overall, the Khelo India
Program aims to create a mass movement that supports youth engagement in
sports, aspiring to elevate India among the top sporting nations.
Fit India Movement
Launched on August 29,
2019, by the Hon’ble Prime Minister, the Fit India Movement seeks to
make fitness an essential aspect of daily life.
Mission
The mission of the Fit India
Movement is to instigate positive behavioral changes and promote the adoption
of a physically active and healthy lifestyle among citizens.
Objectives
To realize its mission, the
Fit India Movement proposes several initiatives aimed at:
- Promoting Fitness: Making fitness accessible, enjoyable, and free
for everyone.
- Awareness Campaigns: Spreading knowledge about fitness and various
physical activities through targeted campaigns.
- Encouraging Indigenous Sports: Highlighting and promoting traditional sports.
- Widespread Reach: Ensuring fitness initiatives reach schools,
colleges, villages, and panchayats.
- Community Engagement: Creating platforms for citizens to share
fitness insights and personal stories to inspire others.





0 Comments